
Class 12 Income Method Solutions | Prepared by CHK Students
Understanding national income is one of the most crucial parts of Class 12 Economics, and among the three main methods, the Income Method holds great importance in board examinations as well as competitive exams. To make your preparation simple and effective, our CHK Student Keshav Khandelwal has carefully prepared these step-by-step solutions for the Income Method.
What is the Income Method?
The Income Method of calculating national income focuses on the earnings received by the factors of production in an economy. It involves summing up all factor incomes like rent, wages, interest, and profit earned within a given period.
Mathematically,
National Income = Compensation of Employees + Rent + Interest + Profit + Mixed Income of Self-Employed
Steps in Solving Income Method Questions
-
Identify Factor Incomes – Wages & salaries, rent, interest, profit, and mixed income.
-
Exclude Transfer Incomes – Like pensions, donations, or gifts, as they are not factor incomes.
-
Adjust for Depreciation & Taxes – Add subsidies, subtract indirect taxes, and depreciation wherever required.
-
Arrive at National Income – By adding all the net factor incomes at factor cost.
Here’s the Solutions –
1. Calculate a) Operating Surplus, and b) Domestic Income;
| Items | ₹ in Crore |
| i) Compensation of Employees | 2,000 |
| ii) Rent and interest | 800 |
| iii) Indirect Taxes | 120 |
| iv) Corporation tax | 460 |
| v) Consumption of fixed capital | 100 |
| vi) Subsidies | 20 |
| vii) Dividend | 940 |
| viii) Undistributed Profits | 300 |
| ix) Net Factor Income to abraod | 150 |
| x) Mixed Income | 200 |
2. Calculate National Income
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| i) Compensation of employees | 2,000 |
| ii) Profit | 800 |
| iii) Rent | 300 |
| iv) Interest | 250 |
| v) Mixed income of self employed | 7000 |
| vi) Net current transfers to abroad | 200 |
| vii) Net Exports | – 100 |
| viii) Net indirect taxes | 1,500 |
| ix) Net Factor income to abroad | 60 |

3. Calculate Net National Product at Market Price:
| Items | (₹ in thousand crore) |
| 1. Compensation of Employees | 250 |
| 2. Mixed income of self employed | 600 |
| 3. Profit | 80 |
| 4. Rent | 30 |
| 5. Interest | 40 |
| 6. Net factor income to abroad | – 10 |
| 7. Net exports | 15 |
| 8. Consumption of fixed Capital | 20 |
| 9. Net indirect taxes | 10 |
| 10. Net current transfers to abroad | 8 |

4. Calculate National Income:
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Profit | 1,000 |
| 2. Mixed Income of self employed | 15,000 |
| 3. Dividends | 200 |
| 4. Interest | 400 |
| 5. Compensation of employees | 7,000 |
| 6. Net factor income to abroad | 100 |
| 7. consumption of fixed capital | 400 |
| 8. Net exports | – 200 |
| 9. Net Indirect taxes | 800 |
| 10. Net Current transfers to rest of the world | 40 |
| 11. Rent | 500 |

5. Calculate the Gross National Product at Market Price:
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Compensation of employees | 2500 |
| 2. Profit | 700 |
| 3. Mixed income of self employed | 7500 |
| 4. Government final consumption expenditure | 3000 |
| 5. Rent | 400 |
| 6. Interest | 350 |
| 7. Net factor income from abroad | 50 |
| 8. Net current transfers to abroad | 100 |
| 9. Net indirect taxes | 150 |
| 10. Depreciation | 70 |
| 11. Net exports | 40 |

6. Calculate the Net National Product at Market Price
| Items | (₹ in Crore) |
| 1. Mixed income of self Employed | 8000 |
| 2. Depreciation | 200 |
| 3. Profit | 1000 |
| 4. Rent | 600 |
| 5. Interest | 700 |
| 6. Compensation of employees | 3000 |
| 7. Net indirect taxes | 500 |
| 8. Net factor income to abroad | 60 |
| 9. Net exports | (-) 50 |
| 10. Net current transfers to abroad | 20 |

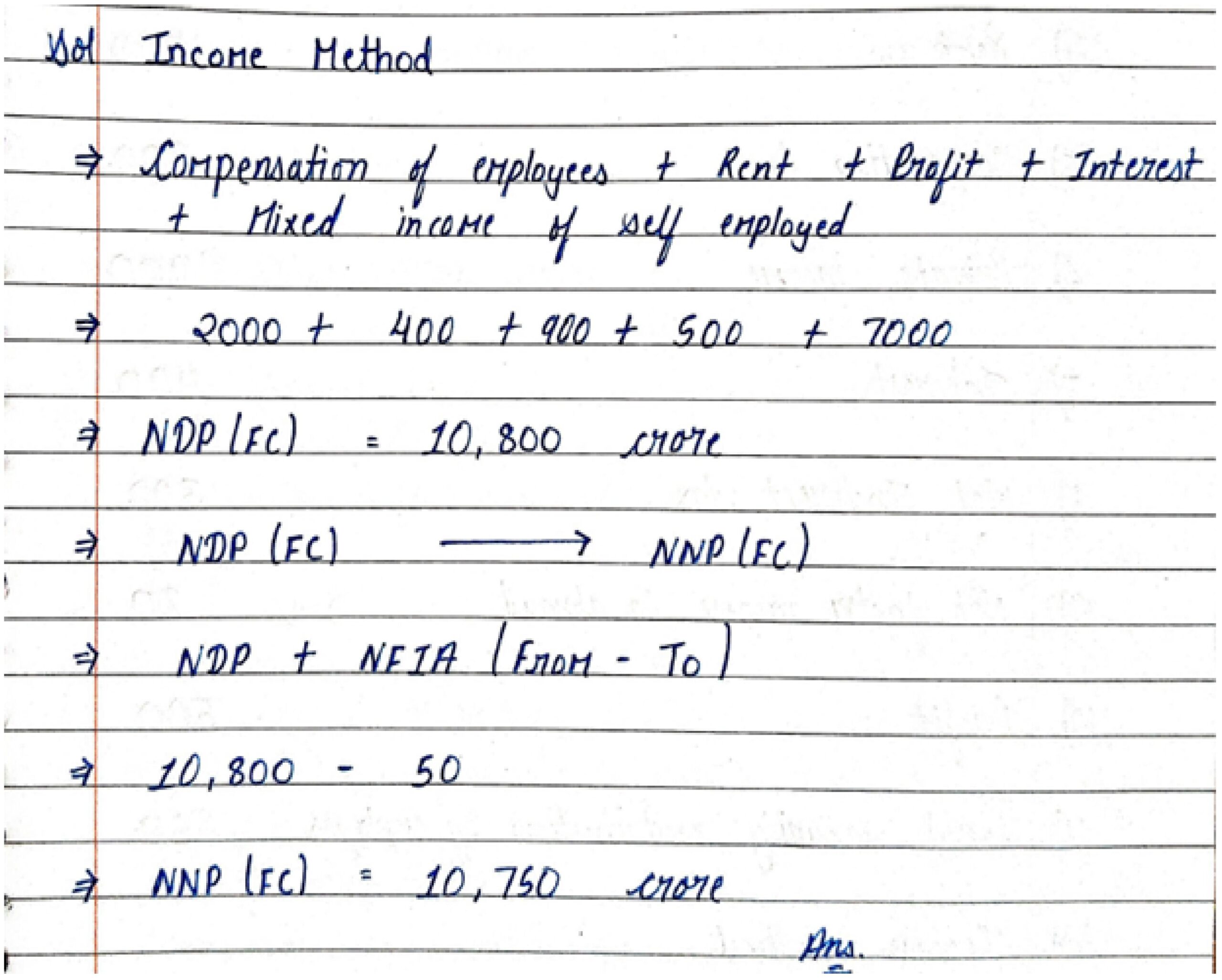
7. Calculate National Income:-
| Items | (₹ in Crore) |
| 1. Compensation of employees | 2000 |
| 2. Rent | 400 |
| 3. Profit | 900 |
| 4. Dividend | 100 |
| 5. Interest | 500 |
| 6. Mixed income of self employed | 7000 |
| 7. Net factor income to abroad | 50 |
| 8. Net exports | 60 |
| 9. Net indirect taxes | 300 |
| 10. Depreciation | 150 |
| 11. Net current transfers to abroad | 30 |
8. Find Net National Product at Market Price:
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Personal taxes | 200 |
| 2. Wage and Salaries | 1200 |
| 3. Undistributed Profit | 50 |
| 4. Rent | 300 |
| 5. Corporation tax | 200 |
| 6. Private Income | 2000 |
| 7. Interest | 400 |
| 8. Net Indirect tax | 300 |
| 9. Net factor income to abroad | 20 |
| 10. Profit | 500 |
| 11. Social Security contributions by employers | 250 |

9. Find Net Domestic Product at Factor cost:
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Rent | 200 |
| 2. Net Current transfers to abroad | 10 |
| 3. National debt interest | 60 |
| 4. Corporate tax | 100 |
| 5. Compensation of employees | 900 |
| 6. Current transfers to government | 150 |
| 7. Interest | 400 |
| 8. Undistributed Profits | 50 |
| 9. Dividend | 250 |
| 10. Net Factor income to abroad | – 10 |
| 11. Income accruing to government | 120 |

10. Find National Income:-
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Wages and Salaries | 1000 |
| 2. Net Current transfers to abroad | 20 |
| 3. Net Factor income paid to abroad | 10 |
| 4. Profit | 400 |
| 5. National debt interest | 120 |
| 6. Social security contributions by employers | 100 |
| 7. Current transfers from government | 60 |
| 8. National income accruing to government | 150 |
| 9. Rent | 200 |
| 10. Interest | 300 |
| 11. Royalty | 50 |

11. Calculate Net National Product at Market Price:-
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Net Factor Income to abroad | – 10 |
| 2. Net current transfers to abroad | 5 |
| 3. Consumption of fixed capital | 40 |
| 4. Compensation of employees | 700 |
| 5. Corporate tax | 30 |
| 6. Undistributed Profits | 10 |
| 7. Interest | 90 |
| 8. Rent | 100 |
| 9. Dividends | 20 |
| 10. Net Indirect tax | 110 |
| 11. Social security contributions by employees | 11 |

12. Calculate the Gross National Product at Market Price:
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Wages and Salaries | 800 |
| 2. Personal tax | 150 |
| 3. Operating Surplus | 200 |
| 4. Undistributed Profits | 10 |
| 5. Social Security contributions by employers | 100 |
| 6. Corporate tax | 50 |
| 7. Net factor income to abroad | – 20 |
| 8. Personal disposable income | 1200 |
| 9. Net indirect tax | 70 |
| 10. Consumption of fixed capital | 30 |
| 11. Mixed income of self employed | 500 |
| 12. Royalty | 9 |

13. Calculate National Income
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Rent | 200 |
| 2. Net Factor income to abroad | 10 |
| 3. National debt interest | 15 |
| 4. Wages and Salaries | 700 |
| 5. Current transfers from government | 10 |
| 6. Undistributed profits | 20 |
| 7. Corporation tax | 30 |
| 8. Interest | 150 |
| 9. Social Security Contributions by employers | 100 |
| 10. Net domestic product accruing to government | 250 |
| 11. Net Current transfers to rest of the world | 5 |
| 12. Dividend | 50 |

14. Calculate ‘Gross National Product at Market Price.
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Rent | 100 |
| 2. Net Current transfers to rest of the world | 30 |
| 3. Social Security contributions by employers | 47 |
| 4. Mixed Income | 600 |
| 5. Gross Domestic Capital Formation | 140 |
| 6. Royalty | 20 |
| 7. Interest | 110 |
| 8. Compensation of Employees | 500 |
| 9. Net Domestic Capital Formation | 120 |
| 10. Net Factor income from abroad | – 10 |
| 11. Net Indirect tax | 150 |
| 12. profit | 200 |

15. Calculate Net Domestic Product at Market Price from the following.
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Income from domestic product accruing to government | 120 |
| 2. Wages and Salaries | 400 |
| 3. National Debt Interest | 60 |
| 4. Profit | 200 |
| 5. Net Factor income to abroad | – 20 |
| 6. Rent | 100 |
| 7. Current transfers from government | 30 |
| 8. Interest | 150 |
| 9. Social Security contribution by employers | 50 |
| 10. Net indirect tax | 70 |
| 11. Net current transfers to abroad | – 10 |

16. Calculate ‘Gross National Product at Market Price from the following.
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Net factor income to abroad | – 10 |
| 2. Net current transfers to abroad | 20 |
| 3. Wages and Salaries | 400 |
| 4. Corporation tax | 50 |
| 5. Profit after corporation tax | 150 |
| 6. Social Security contributions by employers | 50 |
| 7. Rent | 100 |
| 8. Interset | 70 |
| 9. Mixed income of self employed | 300 |
| 10. Net Indirect tax | 140 |
| 11. Consumption of fixed capital | 80 |
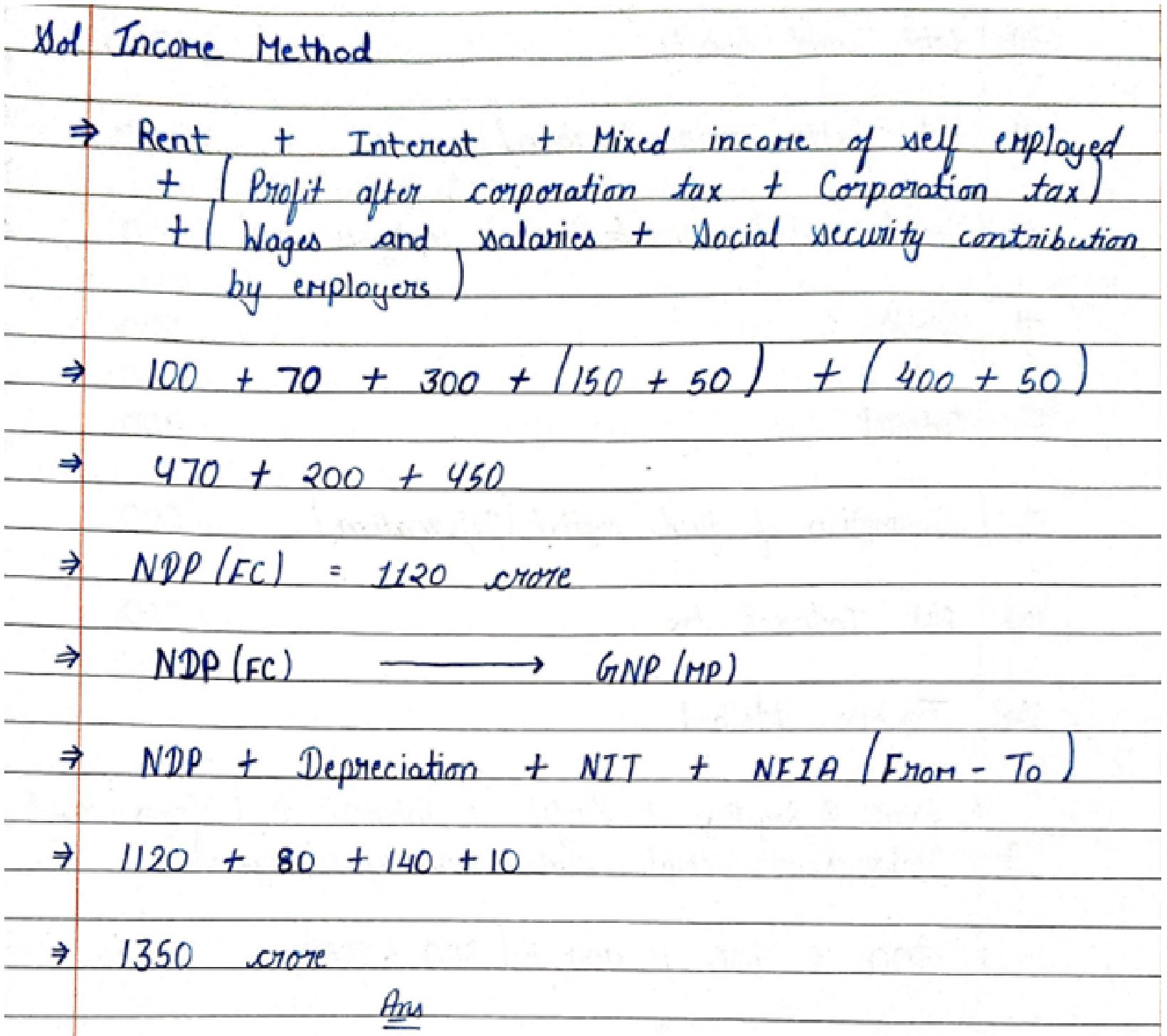
17. Calculate ‘Net National Product at Factor Cost from the following:-
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Social Security contributions by employees | 90 |
| 2. Wages and Salaries | 800 |
| 3. Net Current transfers to abraod | – 30 |
| 4. Rent and Royalty | 300 |
| 5. net factor income to abraod | 50 |
| 6. Social security contributions by employers | 100 |
| 7. Profit | 500 |
| 8. Interest | 400 |
| 9. Consumption of fixed capital | 200 |
| 10. Net indirect tax | 250 |

18. Calculate ‘Net National Product at Factor Cost from the following:-
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. National debt interest | 60 |
| 2. Wages and salaries | 600 |
| 3. Net current transfers to abroad | 20 |
| 4. Rent | 200 |
| 5. Transfer payments by government | 70 |
| 6. Interest | 300 |
| 7. Net domestic product at factor cost accruing to government | 400 |
| 8. Social security contributions by employers | 100 |
| 9. Net factor income paid to abroad | 50 |
| 10. Profits | 300 |

19. From the following data, calculate National Income:-
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Profit | 1500 |
| 2. Rent | 1300 |
| 3. Net Indirect taxes | 350 |
| 4. Mixed income of self employed | 600 |
| 5. Compensation of employees | 3000 |
| 6. Reimbursement to the employees for medical expenses | 300 |
| 7. Depreciation | 200 |
| 8. Excess of factor income to rest of the world over factor income from rest of the world | 50 |
| 9. Excess of imports over exports | 40 |
| 10. Interest | 1100 |

20. Calculate Operating Surplus from the following data:-
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Compensation of employees | 300 |
| 2. Indirect taxes | 200 |
| 3. Consumption of fixed Capital | 100 |
| 4. Subsidies | 50 |
| 5. Gross Domestic Product at market price | 600 |

21. The following information is available for an economy, On the basis of this information using income method, calculate: a) Domestic Income, and b) National Income
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Wages | 10,000 |
| 2. Rent | 5,000 |
| 3. Interest | 400 |
| 4. Dividend | 3,000 |
| 5. Mixed Income | 400 |
| 6. Undistributed profit | 200 |
| 7. Social Security Contribution | 400 |
| 8. Corporate profit tax | 400 |
| 9. Net factor income from abroad | 1000 |

22. Given the following data and using income method calculate:-
a) Net Domestic Income
b) Gross Domestic Income
c) Net National Income
d) Net National Product at Market Price
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Indirect taxes | 9000 |
| 2. Subsidies | 1800 |
| 3. Depreciation | 1700 |
| 4. Mixed Income of self employed | 28000 |
| 5. Operating surplus | 10000 |
| 6. Net factor income from abroad | – 300 |
| 7. Compensation of employees | 24000 |


23. Calculate the national income from the following data:-
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Mixed income of self employed | 200 |
| 2. Old age pension | 20 |
| 3. Dividends | 100 |
| 4. Operating surplus | 900 |
| 5. Wages and Salaries | 500 |
| 6. Profits | 400 |
| 7. Employer’s contribution to social security schemes | 50 |
| 8. Net factor income from abroad | – 10 |
| 9. Consumption of fixed capital | 50 |
| 10. Net indirect tax | 50 |

24. Calculate National Income from the following data:-
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Rent | 80 |
| 2. Interest | 100 |
| 3. Profits | 210 |
| 4. Tax on Profits | 30 |
| 5. Employee’s contribution to social security schemes | 25 |
| 6. Mixed income of self employed | 250 |
| 7. Net indirect tax | 60 |
| 8. Employer’s contributions to social security schemes | 50 |
| 9. Compensation of employees | 500 |
| 10. Net factor income from abroad | – 20 |

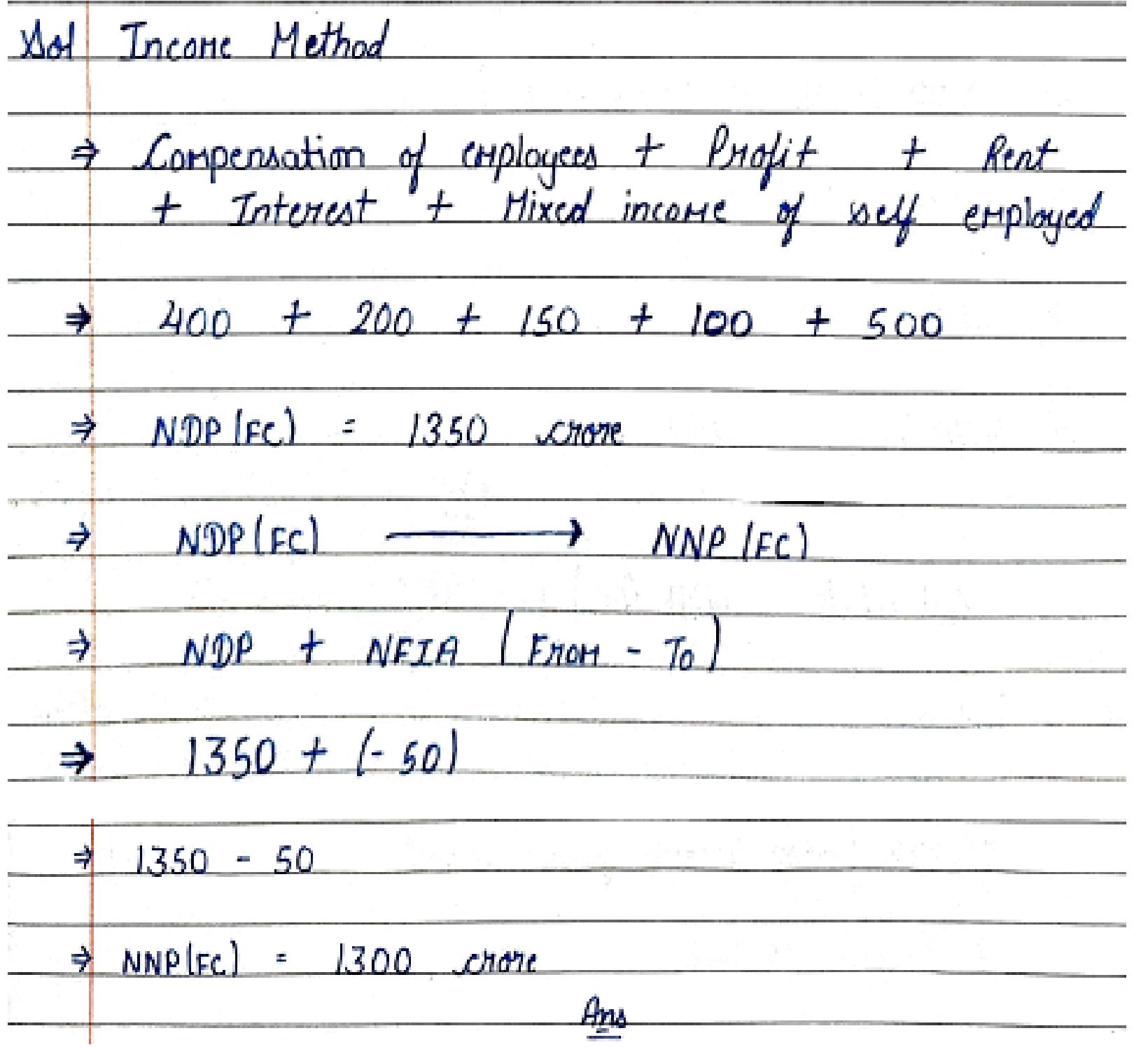
25. Calculate National Income from the following data:-
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Compensation of employees | 400 |
| 2. Profits | 200 |
| 3. Rent | 150 |
| 4. Interest | 100 |
| 5. Dividends | 120 |
| 6. Employer’s contributions to social security schemes | 40 |
| 7. Mixed income of self employed | 500 |
| 8. Direct tax | 100 |
| 9. Net factor income from abroad | – 50 |
26. From the following data, calculate Gross National Product at Market prices:-
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Undistributed profits of private corporate enterprises | 200 |
| 2. Rent | 400 |
| 3. Interest | 200 |
| 4. Profits | 600 |
| 5. Dividends | 300 |
| 6. Wages and Salaries | 225 |
| 7. Net exports | – 20 |
| 8. Net indirect tax | 70 |
| 9. Consumption of fixed capital | 30 |
| 10. Compensation of employees | 250 |
| 11. Mixed income of self employed | 100 |
| 12. Net factor income from abroad | – 10 |

27. Calculate national income from the following data:
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Interest | 50 |
| 2. Corporate tax | 10 |
| 3. Net indirect tax | 40 |
| 4. Rent | 20 |
| 5. Dividends paid | 30 |
| 6. Compensation of employees | 200 |
| 7. Consumption of fixed capital | 15 |
| 8. Undistributed profits | 5 |
| 9. Net factor income received from abroad | – 5 |
| 10. Royalty | 10 |

28. Calculate GDP at MP and GNP at FC from the following data:-
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Operating Surplus | 700 |
| 2. Profit | 100 |
| 3. Wages and Salaries (cash) | 1000 |
| 4. Interest | 200 |
| 5. Consumption of fixed capital | 50 |
| 6. Net factor income from abroad | – 10 |
| 7. Value of benefits in kind provided to employees | 200 |
| 8. Goods and service tax | 150 |
| 9. Subsidies | 10 |


29. Calculate GNP at MP:-
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Mixed income of the self employed | 800 |
| 2. Consumption of fixed capital | 50 |
| 3. Wage and salaries | 700 |
| 4. Compensation of employees from abroad | 20 |
| 5. Rent on land | 200 |
| 6. Royalty of sub soil assets | 30 |
| 7. Interest paid by production units | 150 |
| 8. Interest paid by consumers | 100 |
| 9. Profits | 300 |
| 10. Social security contribution by employers | 100 |
| 11. Property and entrepreneurial income from abroad | – 20 |
| 12. Net indirect tax | 200 |

30. Calculate GDP at MP
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. Dividend paid | 20 |
| 2. Depreciation | 25 |
| 3. Rent | 75 |
| 4. Interest | 125 |
| 5. Undistributed profits | 50 |
| 6. Subsidies | 10 |
| 7. Goods and services tax (GST) | 40 |
| 8. Corporation tax | 30 |
| 9. Mixed Income | 500 |
| 10. Net factor income from abroad | – 20 |
| 11. Compensation of employees | 300 |

31. Calculate Operating Surplus
| Items | (₹ in crore) |
| 1. GNP at market price | 1000 |
| 2. Wages and Salaries | 400 |
| 3. Consumption of fixed capital | 50 |
| 4. Net factor income to abroad | – 10 |
| 5. GST | 100 |
| 6. Social security contributions by employees | 60 |
| 7. Subsidies | 20 |
| 8. Mixed income of the self employed | 200 |
| 9. Interest | 40 |
| 10. Social security contribution by employers | 100 |

Also download – Class 12 Expenditure Method Solutions
Why you should Study with CHK Solutions?
✅ Simplified Explanations – Step-by-step breakdown for every type of question.
✅ Board-Oriented Approach – Designed as per CBSE guidelines.
✅ Exam-Ready Practice – Covers previous year questions and important expected questions.
✅ Student-Friendly Language – Easy to grasp, even in complex numerical problems.
Conclusion
The Income Method might look tricky at first, but with the right guidance and structured solutions, you can master it with ease. The CHK Students’ prepared notes and solutions are the perfect support for your Class 12 Economics preparation.
for more information contact us –
Ph. No. – +91-6367885579
WhatsApp – Click to chat
facebook – @commercehubkota
Instagram – @comerc_classes
Youtube – @commercehubkota
Telegram – @comerc.in










